
Most holographic grating masters are generated initially with a symmetric groove profile. It is important to note that a symmetric profile holographic diffraction grating will only have symmetry in efficiency on either side of zero order when the light is incident at 0 degrees (normal incidence). Blazing is not as easy with holographic gratings however, and with certain notable exceptions, they will not be as efficient as ruled, blazed gratings. Holographic master gratings generally exhibit better stray light properties than ruled master gratings. The addition of a reflective overcoat completes the process. After development, the sinusoidal variation in light intensity during exposure is transformed into a physical structure of the same profile. The resulting interference pattern differentially exposes the photoresist. Holographic master gratings are produced by exposing a thin layer of photoresist to 2 intersecting coherent, monochromatic beams. The resulting profile will show some peak round-off, and not achieve theoretical depth. Actual groove depth is typically 90% of theoretical. As a result, there is some displacement and deformation of the material on the short facet into the previously ruled groove every time a new groove is formed.
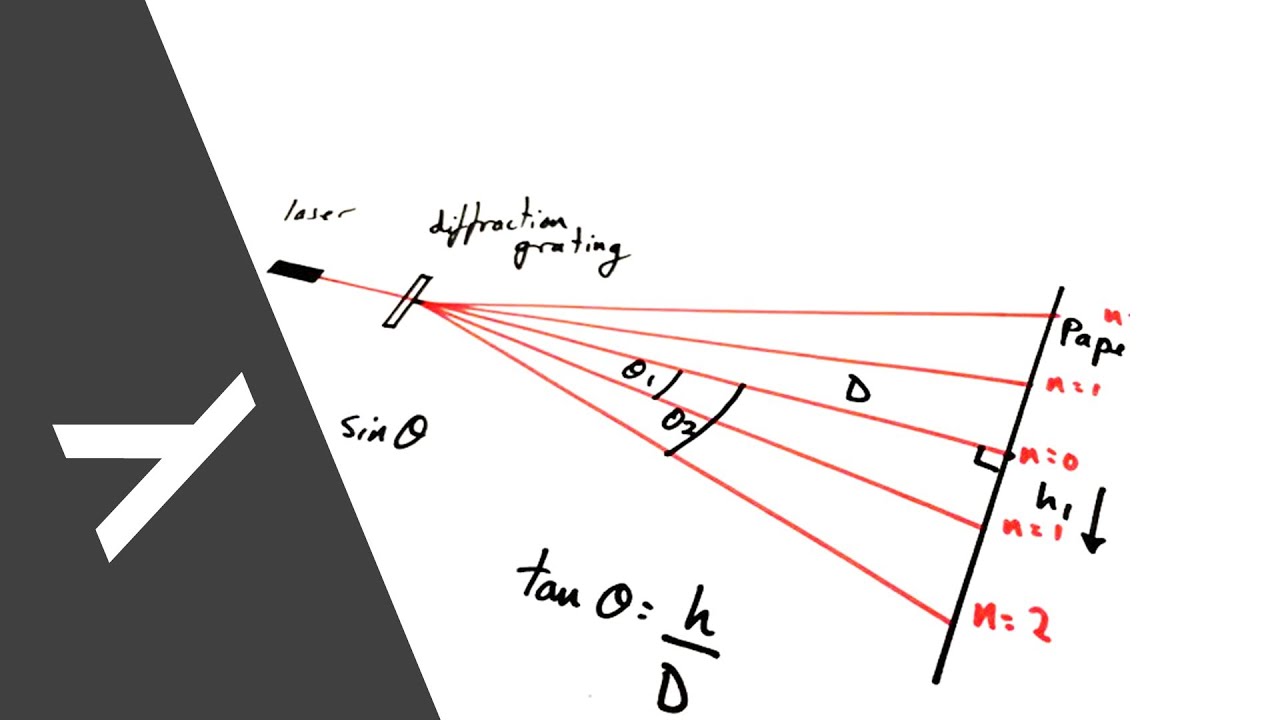
Rather, the coating is burnished by the tool. When a master ruled grating is generated, the diamond tool does not actually remove material and cut a theoretically shaped groove. The calculated theoretical groove depth is given as: Theoretical Profile of a Ruled Blazed Grating Because of the mechanical nature of the mastering process however, there can be random and periodic spacing errors that could detract from the purity of the diffracted spectra. Ruled blazed gratings are very efficient, and are generally the best choice for applications requiring high signal strength. The resulting groove profile has a well defined and controllable groove profile that directs energy efficiently into the desired wavelength range. The master gratings are produced by forming the surface of a soft metallic coating with a diamond form tool. Types of Diffraction Gratings Ruled, Blazed Diffraction Gratings Every wavelength undergoes a different phase shift, and as a result, diffracts at a different angle, resulting in a dispersion of broadband light. This redirection (or diffraction) is a result of the phase change of the electromagnetic wave as it encounters the regular, fixed structure of the grating surface. Also notice that the maximum intensity of the double slit is 4 units, the 3-slit case has a maximum intensity of 9 units, and for 4-slits it is 16 units, as we expect when the amplitude increases by one unit with the addition of each slit.A diffraction grating is a passive optical component that redirects light incident upon the surface at an angle that is unique for every wavelength in a given order.

Notice that the bright fringes for any number of slits occur at the same places as for the double slit (provided they have the same slit separation), and that the number of dark fringes between bright fringes goes up by one every time another slit is added. Putting these functions into a graphing calculator confirms what we found above, as well as what we suspect about \(n\) slits – that there are \(n-1\) dark fringes between each maximally-bright fringe.įigure 3.3.3 - Comparison of Interference Patterns by Number of Slits


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
